.NET Mastery
Know all concepts of software development
10/12/2025
.NET Framework relation with Windows Version
.NET Framework
The .NET Framework is a software development platform developed by Microsoft.
Types of .NET Platforms : While ".NET Framework" refers specifically to the original Windows-only version, there are other types in the broader ".NET" ecosystem:
It provides a controlled environment for developing and running applications, primarily on Windows.
It includes a large class library called the Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language interoperability across several programming languages, most notably C#, VB.NET, and F#.
Types of .NET Platforms : While ".NET Framework" refers specifically to the original Windows-only version, there are other types in the broader ".NET" ecosystem:
1. .NET Framework
Platform: Windows-only
Use Case: Legacy enterprise applications, desktop apps
Latest Version: .NET Framework 4.8.1 (as of 2023)
2. .NET Core
Platform: Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux)
Use Case: Modern web apps, microservices
Status: Superseded by .NET 5+
3. .NET (formerly .NET 5 and later)
Platform: Unified and cross-platform
Use Case: Web, desktop, mobile, cloud, gaming, IoT
Latest Version: .NET 8 (as of 2024)
4. Mono/Xamarin
Platform: Mobile and embedded systems
Use Case: iOS and Android apps using C#
Status: Integrated into .NET MAUI
5. .NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI)
Platform: Cross-platform UI framework
Use Case: Build native apps for Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows with a single codebase
Dependency Inversion Principle vs Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection:
A design pattern or technique used to implement DIP by injecting dependencies (like services or repositories) into a class, rather than the class creating them itself.
It is done using Constructor injection, property injection, DI containers(Autofac, Unity, Windsor Castle)
Dependency Inversion Principle
Instead of a class depending directly on another concrete class, it should depend on an interface or abstract class.This makes your code flexible, testable, and maintainable.
Easy to switch implementations (e.g., Service1, Service2). Easy to test using mocks. Follows DIP and promotes clean architecture
interface IService
{
public void ResetDevice();
}
public class Service1 : IService
{
public void ResetDevice() {// Sercice1 logic}
}
public class Service2 : IService
{
public void ResetDevice() {// Service2 logic}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
IService service;
if(_soapVersion <= 1)
service = new Service1();
else
service = new Service2(); //easily replaceable, swithable
}
}
Without LSP:
Why the name inversion - The word "inversion" in Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP) refers to a reversal of the conventional direction of dependency in software design.
Without DIP: High-level modules (like business logic) depend on low-level modules (like database or email services).
This means the flow of control and design is top-down, and high-level logic is tightly coupled to implementation details.
With DIP: Both high-level and low-level modules depend on abstractions (interfaces or abstract classes).
The control is inverted: instead of high-level modules controlling low-level ones directly, they rely on abstractions that are implemented by low-level modules. - loosly coupled
Instead of a class depending directly on another concrete class, it should depend on an interface or abstract class.This makes your code flexible, testable, and maintainable.
Easy to switch implementations (e.g., Service1, Service2). Easy to test using mocks. Follows DIP and promotes clean architecture
interface IService
{
public void ResetDevice();
}
public class Service1 : IService
{
public void ResetDevice() {// Sercice1 logic}
}
public class Service2 : IService
{
public void ResetDevice() {// Service2 logic}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
IService service;
if(_soapVersion <= 1)
service = new Service1();
else
service = new Service2(); //easily replaceable, swithable
}
}
Without LSP:Without DIP: High-level modules (like business logic) depend on low-level modules (like database or email services). This means the flow of control and design is top-down, and high-level logic is tightly coupled to implementation details.
With DIP: Both high-level and low-level modules depend on abstractions (interfaces or abstract classes). The control is inverted: instead of high-level modules controlling low-level ones directly, they rely on abstractions that are implemented by low-level modules. - loosly coupled
3/16/2025
IoC vs DI vs DIP
1.Inversion of Control (IoC)
A fundamental principle that inverts traditional control flow
Enables decoupling of components from their dependencies
Provides flexibility in how objects are created and managed
Enables decoupling of components from their dependencies
Provides flexibility in how objects are created and managed
2.Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
A design guideline that specifies how modules should relate
Ensures high-level modules don't depend directly on low-level ones
Promotes abstraction-based relationships
3.Dependency Injection (DI)
A concrete technique for implementing IoC
Provides a specific mechanism for delivering dependencies
Helps achieve the goals outlined by DIP
IoC is the broad principle that enables various patterns, DIP guides how modules relate to each other, and DI provides a specific technique for implementing both concepts. Together, they form a powerful foundation for building maintainable software systems.
3/15/2025
Liskov Substitution Principle
Without LSP:Example, we are creating different robots, Kawasaki, Yaskawa, and ABBRobots all inheriting IRobots and have methods like Connect(), Operate() , Move(). Later say some new functionality in ABBRobots like ReportFaultData() is introduced, so we need to added ReportFaultData() in interface and other robots should do " throw NotSupportedException("Reporting fault data is not supported");" , this leads to compile time error or we need to do nothing, and so we need to change other classes.
With LPS:Instead we will create new interface ISupportsFaultDataReporting and add the new ReportFaultData() and inherit only for ABBRobots
public class ABBRobots : IRobots, ISupportsFaultDataReporting
{
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
List robots = new List{new Kawasaki(),new Yaskawa(),new ABBRobots()};
foreach (var robot in robots)
{
robot.Move();
if (robot is ISupportsFaultDataReporting faultDataReportingRobot)
{
faultDataReportingRobot.Report();
}
}
}
}
Without LSP:
Why the name substitution - The idea is that you should be able to substitute the base class with the derived class without breaking the functionality.
// Substituting base class with dereived class
Shape shape = new Rectangle(5, 10);
Without LSP:
Example, we are creating different robots, Kawasaki, Yaskawa, and ABBRobots all inheriting IRobots and have methods like Connect(), Operate() , Move(). Later say some new functionality in ABBRobots like ReportFaultData() is introduced, so we need to added ReportFaultData() in interface and other robots should do " throw NotSupportedException("Reporting fault data is not supported");" , this leads to compile time error or we need to do nothing, and so we need to change other classes.
With LPS:
Instead we will create new interface ISupportsFaultDataReporting and add the new ReportFaultData() and inherit only for ABBRobots
public class ABBRobots : IRobots, ISupportsFaultDataReporting
{
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
List robots = new List{new Kawasaki(),new Yaskawa(),new ABBRobots()};
foreach (var robot in robots)
{
robot.Move();
if (robot is ISupportsFaultDataReporting faultDataReportingRobot)
{
faultDataReportingRobot.Report();
}
}
}
}
Without LSP:
Why the name substitution - The idea is that you should be able to substitute the base class with the derived class without breaking the functionality.
// Substituting base class with dereived class
Shape shape = new Rectangle(5, 10);
2/07/2013
Model,View and View Model Patern (M V VM pattern)
The MVVM Pattern
The Model-View-ViewModel pattern can be used on all XAML platforms. Its intent is to provide a clean separation of concerns between the user interface controls and their logic.There are three core components in the MVVM pattern: the model, the view, and the view model. Each serves a distinct and separate role. The following illustration shows the relationships between the three components.
The components are decoupled from each other, thus enabling:
- Components to be swapped
- Internal implementation to be changed without affecting the others
- Components to be worked on independently
- Isolated unit testing
The view model isolates the view from the model classes and allows the model to evolve independently of the view.
View
The view is responsible for defining the structure, layout, and appearance of what the user sees on the screen. Ideally, the view is defined purely with XAML, with a limited code-behind that does not contain business logic.In a Windows Phone application, a view is typically a page in the application. In addition, a view could be a sub-component of a parent view, or a DataTemplate for an object in an ItemsControl.
A view can have its own view model, or it can inherit its parent's view model. A view gets data from its view model through bindings, or invoking methods on the view model. At run time, the view changes when UI controls respond to view model properties raising change notification events.
There are several options for executing code on the view model in response to interactions on the view, such as a button click or item selection. If the control is a Command Source, the control’s Command property can be data-bound to an ICommand property on the view model. When the control’s command is invoked, the code in the view model will be executed. In addition to commands, behaviors can be attached to an object in the view and can listen for either a command to be invoked or event to be raised. In response, the behavior can then invoke an ICommand on the view model or a method on the view model.
Model
The model in MVVM is an implementation of the application's domain model that includes a data model along with business and validation logic. Examples of model objects include repositories, business objects, data transfer objects (DTOs), Plain Old CLR Objects (POCOs), and generated entity and proxy objects.View Model
The view model acts as an intermediary between the view and the model, and is responsible for handling the view logic. Typically, the view model interacts with the model by invoking methods in the model classes. The view model then provides data from the model in a form that the view can easily use. The view model retrieves data from the model and then makes the data available to the view, and may reformat the data in some way that makes it simpler for the view to handle. The view model also provides implementations of commands that a user of the application initiates in the view. For example, when a user clicks a button in the UI, that action can trigger a command in the view model. The view model may also be responsible for defining logical state changes that affect some aspect of the display in the view, such as an indication that some operation is pending.In order for the view model to participate in two-way data binding with the view, its properties must raise the PropertyChanged event.
View models satisfy this requirement by implementing the INotifyPropertyChanged interface and raising the PropertyChanged event when a property is changed. Listeners can respond appropriately to the property changes when they occur.
For collections, the view-friendly System.Collections.ObjectModel.ObservableCollection<T> is provided. This collection implements collection changed notification, relieving the developer from having to implement the INotifyCollectionChanged interface on collections.
Connecting View Models to Views
MVVM leverages the data-binding capabilities in Silverlight to manage the link between the view and view model, along with behaviors and event triggers. These capabilities limit the need to place business logic in the view's code-behind.There are many approaches to connecting a view model to a view, including direct relations and container-based approaches. However, all share the same aim, which is for the view to have a view model assigned to its DataContext property.
Views can be connected to view models in a code-behind file, or in the view itself.
Code-Behind
A view can have code in the code-behind file that results in the view model being assigned as its DataContext property. This could be as simple as a view instantiating a new view model and assigning it to its DataContext, or injecting a view model into a view using an inversion-of-control container.However, connecting a view model to a view in a code-behind file is discouraged as it can cause problems for designers in both Visual Studio and Microsoft Expression Blend® design software.
View
If a view model does not have any constructor arguments, the view model can be instantiated in the view as the view’s DataContext. A common approach to doing this is to use a view model locator. This is a resource which exposes the application’s view models as properties that individual views can data bind to. This approach means that the application has a single class that is responsible for connecting view models to views. In addition, it still leaves developers free to choose to manually perform the connection within the view model locator, or by using a dependency injection container.The Benefits of MVVM
MVVM enables a great developer-designer workflow, providing these benefits:- During the development process, developers and designers can work more independently and concurrently on their components. The designers can concentrate on the view, and if they are using Expression Blend, they can easily generate sample data to work with, while the developers can work on the view model and model components.
- The developers can create unit tests for the view model and the model without using the view. The unit tests for the view model can exercise exactly the same functionality as used by the view.
- It is easy to redesign the UI of the application without touching the code because the view is implemented entirely in XAML. A new version of the view should work with the existing view model.
- If there is an existing implementation of the model that encapsulates existing business logic, it may be difficult or risky to change. In this scenario, the view model acts as an adapter for the model classes and enables you to avoid making any major changes to the model code.
read more : http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848246.aspx
1/01/2013
Semantic Web in plain english
The semantic web is about making computers behave (or ‘think’) more like humans. The easiest way to understand what this means is to use a cooking analogy. Think of each website where you put your content as a big cookpot. You might throw a carrot into one pot and tag it ‘carrot’, and into another you might put some spaghetti and tag it ‘pasta’. Computers are fine with this kind of input.
But what computers can’t do yet is understand that the thing you called ‘carrot’ is a root vegetable, is full of Vitamin A – and that you are making minestrone soup. It also doesn’t know that you have another pot simmering, and that there’s pasta in there. Or that you need to make a sauce for it. This kind of thinking requires context, and an ability to see the big picture – that is, to know what’s in each pot, and to understand that you’re making dinner. That’s all that data-meshing is; it’s about applying meaning to information from different sources. This is what the semantic web is all about; I call it the “web of meaning” or the “contextual web”. It means being able to ask your computer everything from “When did I last have Sally over?” to “Can I afford a new laptop this month?”.
11/21/2012
cannot be opened because its project type (.csproj) is not supported by this version of the application.
Go to Start> All Programs > Visual Studio 2008 > Visual Studio Tools > Click Visual Studio 2008 Command Prompt. Type the below command and press enter.
devenv.exe /resetskippkgs
devenv.exe /resetskippkgs
8/27/2012
SQL Delete current database
I need to delete my current database which I am using it , I googled around and found this answer:
http://sqlserver2000.databases.aspfaq.com/how-do-i-drop-a-sql-server-database.html
ALTER DATABASE myDataBase
SET SINGLE_USER
WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
DELETE DATABASE myDataBase
http://sqlserver2000.databases.aspfaq.com/how-do-i-drop-a-sql-server-database.html
ALTER DATABASE myDataBase
SET SINGLE_USER
WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
DELETE DATABASE myDataBase
8/26/2012
Password protect your outlook
This link guides you, how to protect your Outlook with password :
http://www.groovypost.com/howto/password-protect-outlook-pst-file/
http://www.groovypost.com/howto/password-protect-outlook-pst-file/
8/16/2012
C# difference between StringBuilder and String Object
The most common operation with string is concatenation, and this has to be performed very efficiently.
When we use String objects to concatenate two strings , then a new copy of string object is created in memory by adding two objects , and the old string object is deleted.
So we use StringBuilder to do it in a effective way, here the concatenation is done on the exsisting string, hence the insertion is faster. Concatenation is done using Append() method
When we use String objects to concatenate two strings , then a new copy of string object is created in memory by adding two objects , and the old string object is deleted.
So we use StringBuilder to do it in a effective way, here the concatenation is done on the exsisting string, hence the insertion is faster. Concatenation is done using Append() method
8/02/2012
Difference between null and String.Empty
1. string statement=null : means no object exists; null is not a value, it is a state indicating that object value is unknown or does not exists.
2. string statement = String.Empty : use of string.Empty doesn't create any objects while "" creates a string object. So using string.Empty is better than using "" because every time you use "", it creates a new string while string.Empty just reference s string in memory that is created by default.
8/01/2012
Understanding Reflection and static constructor
Hi .net newbies,
This post is mostly for you !!, to understand what Reflection and static constructor really mean ,and when are they used in .net projects.
This post is mostly for you !!, to understand what Reflection and static constructor really mean ,and when are they used in .net projects.
You would have learnt what does .net reflection and static constructor mean ,
You may say reflection is : The process of obtaining information about the assemblies and the types defined within them ,and creating and invoking and accessing type instance at run time and
You may say static constructor is used to initialize any static data or to perform a certain action that needs to be performed once.
So when do you use Reflection or static constructor, the below picture answers the question:
7/23/2012
WCF as Windows Services Step by Step example
Hi Guys, in this post I will be explaining how to create a simple WCF service and host it as a 'Windows Service'.
Lets create a simple Windows Service which has a OperationContract which will add numbers and return it
Step 1: Create a simple WCF service library
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
Step 1: Create simple WCF Service library:
1. Open Visual Studio 2010 , Create new project and choose Windows Service Library named as Wcf_WindowsService_Add
2. Delete these files: App.config, IService1.cs, Service1.cs, and create your own WCF Service, Right click your project and create new item - > WCF Service name it as WindowsServiceAdd.cs

3. In app.config files you can see two endpoints with bindings wsHttpBinding and mexHttpBinding and with abase address
4. Open IWindowsServiceAdd.cs Interface remove Dowork() Contract and your Contract with name Add()
5. Open WindowsServiceAdd.cs remove DoWork() and define your Add() OperationContract :
6. Build your project , now your WCF Service library dll is ready to use.
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service:
1. Right Click your solution and create new project. -> Windows -> Windows Services.
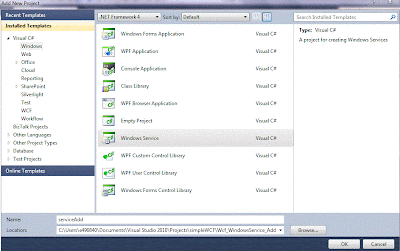
2. Delete Program.cs and Service1.cs and create your own Service , by right clicking the project add new item -> Windows Service

3. Click 'click here to switch to code view' , and modify the code as shown below to add a Service Host and methods to stop and start the services ,and add System.ServiceModel to your project , and your Service Library dll too
4. Add Program.cs file
5.Build this project . now it is ready to be installed in your machine
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
1. Inorder to install the service we need Installer class, so add new installer class:
2.Goto Start - > All programs -> Visual Studio 2010 - > Visual Studio Tools -> Visual Studio command prompt. Goto to path of your serviceAdd.exe , and install it using ' installutil serviceAdd.exe
3. You can see your service in Service Console
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
1. Start your service , Create a new Windows Form project, refer your WCF hosted as Windows services ( http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/Wcf_WindowsService_Add/WindowsServiceAdd/ ) to this project. add a lable and a button, double click the button and and add the bellow code , and run your project :
2. Build and Run your Windows Form to consume the service
Lets create a simple Windows Service which has a OperationContract which will add numbers and return it
Step 1: Create a simple WCF service library
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service
Step 3: Install the Windows Service
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
Step 1: Create simple WCF Service library:
1. Open Visual Studio 2010 , Create new project and choose Windows Service Library named as Wcf_WindowsService_Add

3. In app.config files you can see two endpoints with bindings wsHttpBinding and mexHttpBinding and with abase address
4. Open IWindowsServiceAdd.cs Interface remove Dowork() Contract and your Contract with name Add()
5. Open WindowsServiceAdd.cs remove DoWork() and define your Add() OperationContract :
6. Build your project , now your WCF Service library dll is ready to use.
Step 2: Create a simple Windows Services in which you will host the service:
1. Right Click your solution and create new project. -> Windows -> Windows Services.

2. Delete Program.cs and Service1.cs and create your own Service , by right clicking the project add new item -> Windows Service

3. Click 'click here to switch to code view' , and modify the code as shown below to add a Service Host and methods to stop and start the services ,and add System.ServiceModel to your project , and your Service Library dll too
4. Add Program.cs file
5.Build this project . now it is ready to be installed in your machine
1. Inorder to install the service we need Installer class, so add new installer class:
2.Goto Start - > All programs -> Visual Studio 2010 - > Visual Studio Tools -> Visual Studio command prompt. Goto to path of your serviceAdd.exe , and install it using ' installutil serviceAdd.exe
Step 4: Consume the Windows Services in a Windows Form Client.
1. Start your service , Create a new Windows Form project, refer your WCF hosted as Windows services ( http://localhost:8732/Design_Time_Addresses/Wcf_WindowsService_Add/WindowsServiceAdd/ ) to this project. add a lable and a button, double click the button and and add the bellow code , and run your project :
2. Build and Run your Windows Form to consume the service
6/19/2012
SQL Constraints
Constraints limit the type of data that can go into the table.
The following are the constraints:
The following are the constraints:
- NOT NULL
- UNIQUE
- PRIMARY KEY
- FOREIGN KEY
- CHECK
- DEFAULT
6/18/2012
SQL Joins
Hi newbies,
Want to learn SQL joins at a glance!!, here you go... SQL joins is Venn diagram representation:
A very nice picture given in codeproject.
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/33052/Visual-Representation-of-SQL-Joins
Want to learn SQL joins at a glance!!, here you go... SQL joins is Venn diagram representation:
A very nice picture given in codeproject.
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/33052/Visual-Representation-of-SQL-Joins
5/13/2012
What are EXD files
EXD is control information cache file . It is a type of file that contains your most recently used information of a computer object , which in this case is a control
read more
read more
1/30/2012
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)










